Battery storage charge, discharge and warranty explained

Battery storage charge, discharge and warranty explained
Charging:
Charging a solar PV battery storage system involves the transfer of electricity from an external power source, such as solar panels or the grid, to the battery unit. During periods of ample sunlight or low energy demand, surplus electricity generated by solar panels is directed towards the battery for storage ready to use later in the day. This process involves converting the electrical energy into a chemical form that can be stored within the battery cells. The charging cycle typically occurs when the battery's state of charge (SoC) is below a preset level, ensuring that the battery is ready to supply power when needed. Charging your battery or batteries from solar panels is the most cost-effective way but you can also charge your batteries from the grid during off-peak hours, when electricity rates are typically lower allowing you to store energy at a more cost-effective rate. You can then use this stored energy during peak hours when electricity prices are higher, effectively reducing your overall energy expenses. One aspect of charging from the grid you need to be careful of is to avoid charging your batteries too high so that when the solar pv is generating the batteries become full resulting in exporting generation back to the grid at a lower rate. Charging from the grid has higher benefits in the winter months and can be a huge benefit to lowering your electricity bills.
People often ask how long it will take to charge up a certain sized battery when considering how much battery storage they require but to determine the time it takes to charge, for example, a 5 kWh (kilowatt-hour) battery, you need to consider the charging rate and the power source. Charging time is calculated by dividing the battery capacity (5 kWh) by the charging rate.
For example, if you are charging the 5 kWh battery at a rate of 1 kW (kilowatt), it would take approximately 5 hours to fully charge the battery (5 kWh / 1 kW = 5 hours).
Keep in mind that charging time can vary based on factors such as the efficiency of the charging process, any charging losses, and whether the charging rate remains constant throughout the process due to the solar generation being used in the property. It's also important to note that some battery systems may adjust the charging rate as the battery gets closer to being fully charged to optimize battery health and longevity.
Discharging:
Discharging refers to the release of stored energy from the battery back into the electrical system for use in the household. This occurs when energy demand exceeds the immediate output of solar panels, such as during the evening or peak consumption times. The stored energy is converted from its chemical form back into electricity, which can then power appliances, devices, and lighting within the home or facility. Discharging can also provide backup power during grid outages, ensuring continuous operation of essential loads if required as this doesn’t come as standard with systems and requires additional accessories and earthing.
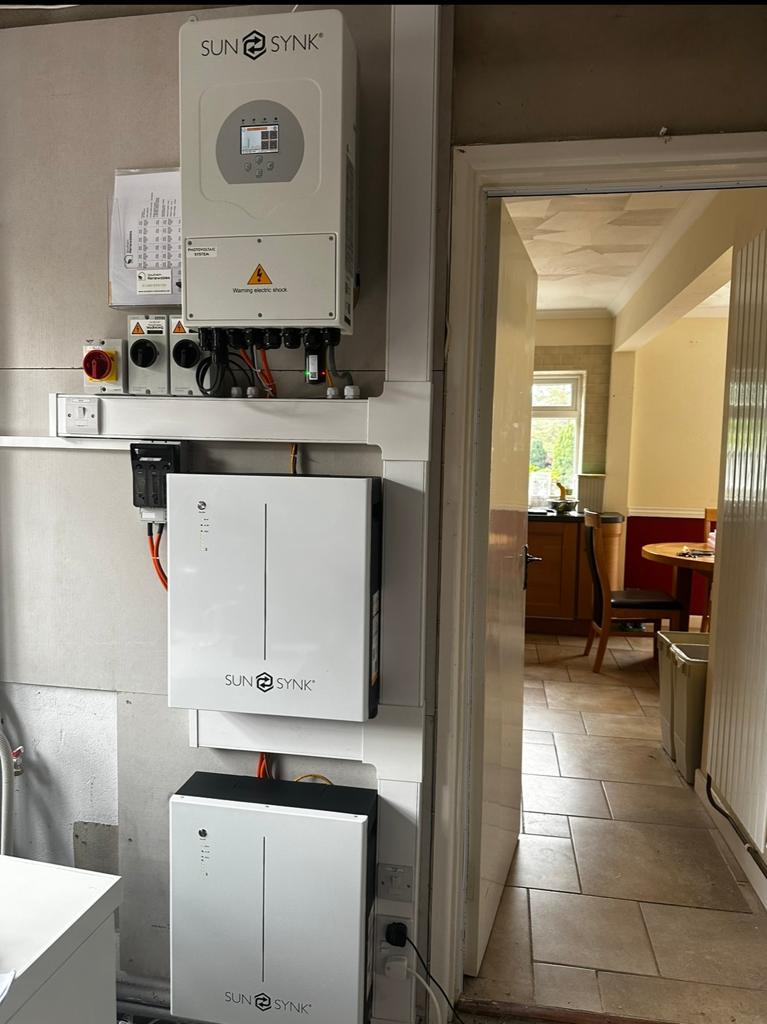
Effective charging and discharging management is crucial for maximising the benefits of a solar PV battery storage system. Advanced control systems monitor energy production, consumption patterns, and battery status to determine optimal times for charging and discharging. This optimisation helps to ensure that energy is stored when it's most abundant and cost-effective, and discharged when it's most valuable, such as during high electricity tariff periods or when the sun isn't shining. For example, Sunsynk inverter to battery communication is very advanced and easy to set up. It provides features that allow you to discharge the batteries to a certain SOC % leaving enough storage for later in the day when the electricity Tarif could be more expensive.
People often ask how long it will take to discharge a certain-sized battery when considering how much battery storage they require. The time it takes for a 5 kWh (kilowatt-hour) battery to discharge depends on the power consumption rate of the devices or appliances using the energy from the battery. Discharge time is calculated by dividing the battery capacity (5 kWh) by the power consumption rate.
For example, if the devices connected to the battery have a combined power consumption of 1 kW (kilowatt), the battery would be depleted in approximately 5 hours (5 kWh / 1 kW = 5 hours). One more factor to consider is DOD (Depth of discharge), which is a safety feature preventing the battery from discharging past a set SOC % giving the battery a longer lifespan. DOD is normally between 10-20% giving a useable capacity of either 80 or 90%
In conclusion, charging and discharging are integral processes within a solar PV battery storage system. They enable the system to capture surplus solar energy during periods of abundance and release it when demand is high or during power outages, contributing to energy efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced energy resilience.
Battery warranty and lifespan
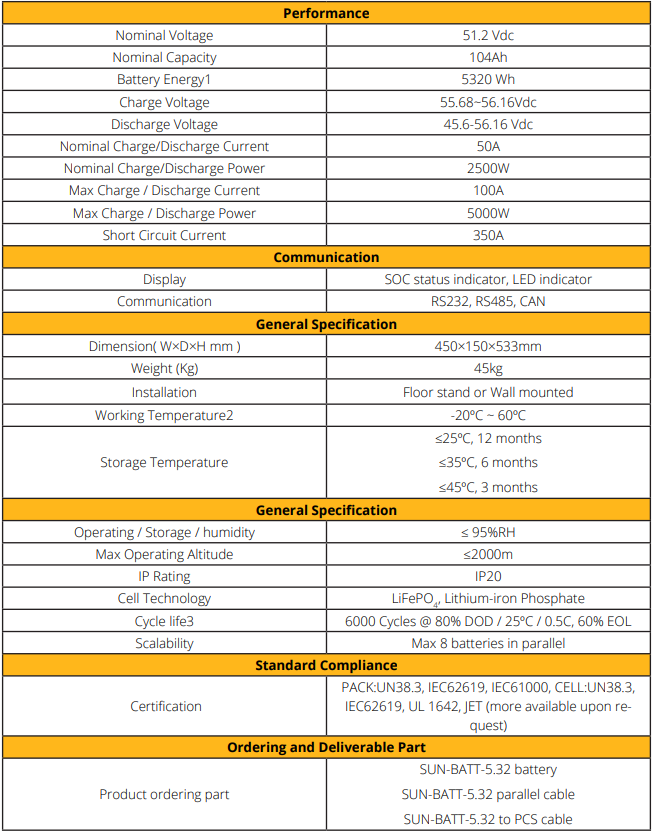
For warranties and estimated lifespan, you should always check the manufactures data sheets and warranty information. On average a battery storage unit will have either a 10-year or 6000 cycle warranty. For example below is a Sunsynk data sheet that shows the settings.